前言 力扣刷题知识笔记和思路记录
刷题指南参考:CyC2018/CS-Notes: :books: 技术面试必备基础知识、Leetcode、计算机操作系统、计算机网络、系统设计https://github.com/CyC2018/CS-Notes/tree/master/
知识点参考:Hello 算法!https://www.hello-algo.com/
一、数组 (1)280-移动零 给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入: nums = [0,1,0,3,12] 输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
示例 2:
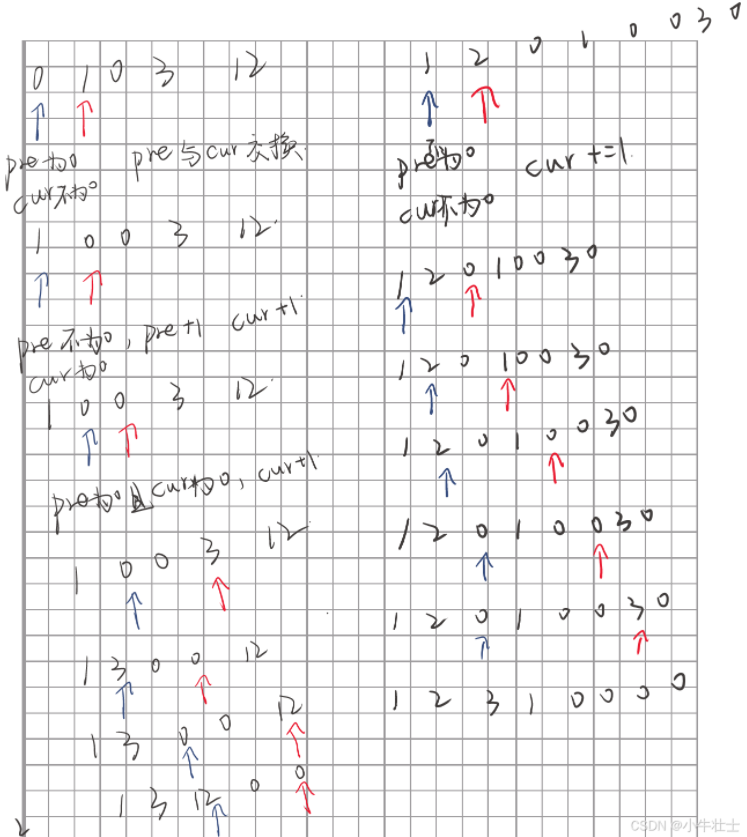
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution (object ): def moveZeroes (self, nums ): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead. """ pre = 0 cur = 1 while cur < len (nums): if nums[pre] == 0 and nums[cur] != 0 : nums[pre],nums[cur] = nums[cur],nums[pre] elif nums[pre] != 0 and nums[cur] == 0 : pre += 1 cur += 1 elif nums[pre] == 0 and nums[cur] == 0 : cur += 1 elif nums[pre] != 0 and nums[cur] != 0 : cur += 1
自己的解法思路:
使用两个指针pre和cur,将指针指向数字是否为零将情况分为4类
①pre=0,cur!=0:pre与cur两个数交换位置,将pre的0移动到后面
②pre!=0,cur!=0:cur+1,寻找下一个0
③pre!=0,cur=0:pre+1,cur+1
④pre=0,cur=0:cur+1,寻找下一个非0
总的来说就是移动pre和cur,交换两个数位置
测试结果似乎移动了原来非零数的相对位置
Testcase
Answer
Expected Answer
次优解:
直接利用python列表内置函数,是0的删除,并且在末尾加0
1 2 3 4 for i in range (len (nums)): if nums[i]==0 : nums.remove(0 ) nums.append(0 )
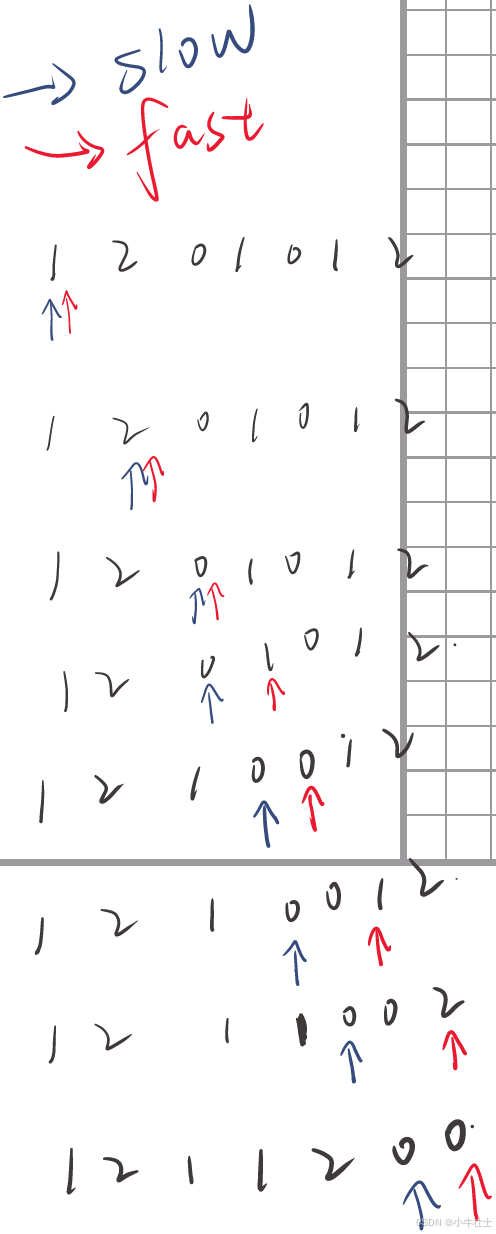
最优解:快慢双指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 slow = 0 for fast in range (len (nums)): if nums[fast]!=0 : nums[fast],nums[slow] = nums[slow],nums[fast] slow += 1
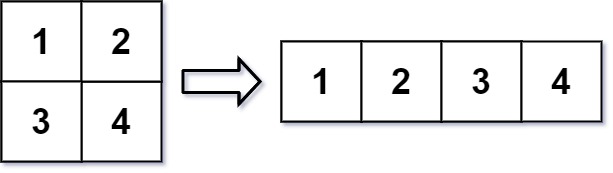
(2)566-重塑举证 在 MATLAB 中,有一个非常有用的函数 reshape ,它可以将一个 m x n 矩阵重塑为另一个大小不同(r x c)的新矩阵,但保留其原始数据。
给你一个由二维数组 mat 表示的 m x n 矩阵,以及两个正整数 r 和 c ,分别表示想要的重构的矩阵的行数和列数。
重构后的矩阵需要将原始矩阵的所有元素以相同的 行遍历顺序 填充。
如果具有给定参数的 reshape 操作是可行且合理的,则输出新的重塑矩阵;否则,输出原始矩阵。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:mat = [[1,2],[3,4]] , r = 1 , c = 4 输出:[[1,2,3,4]]
示例 2:
1 2 输入:mat = [[1,2],[3,4]] , r = 2 , c = 4 输出:[[1,2],[3,4]]
思路:
先创建r×c的0矩阵,依次遍历mat,将0变为对应元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution (object ): def matrixReshape (self, mat, r, c ): """ :type mat: List[List[int]] :type r: int :type c: int :rtype: List[List[int]] """ if r * c != len (mat[0 ]) * len (mat): return mat else : lst = [[] for i in range (r)] for i in lst: for _ in range (c): i.append(0 ) r_index = 0 c_index = 0 for _ in mat: for num in _: print (num) if c_index < c: lst[r_index][c_index] = num c_index += 1 else : r_index += 1 c_index = 0 lst[r_index][c_index] = num c_index += 1 return lst
方法二:
https://link.csdn.net/?from_id=146317665&target=https%3A%2F%2Fleetcode.cn%2Fproblems%2Freshape-the-matrix%2Fsolutions%2F606281%2Fzhong-su-ju-zhen-by-leetcode-solution-gt0g
mat元素索引对
1 ans[x // c][x % c] = nums[x // n][x % n]
(3)485-最大连续1的个数
给定一个二进制数组 nums , 计算其中最大连续 1 的个数。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [1,1,0,1,1,1] 输出:3 解释:开头的两位和最后的三位都是连续 1 ,所以最大连续 1 的个数是 3.
示例 2:
1 2 输入:nums = [1,0,1,1,0,1] 输出:2
思路:
暴力解法遍历,与最大个数count_max作比较,看是否进行替换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution (object ): def findMaxConsecutiveOnes (self, nums ): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: int """ count = 0 count_max = 0 for i in range (len (nums)): if nums[i] == 1 : count += 1 if count > count_max: count_max = count elif nums[i] ==0 : count = 0 return count_max
(3)240-搜索二维矩阵
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 *m* x *n* 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target 。该矩阵具有以下特性:
每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:matrix = , target = 5 输出:true
示例 2:
1 2 输入:matrix = , target = 20 输出:false
二、链表 这里介绍几种形式的链表的增删查改以及列出了题库里面的一些Leetcode例题的解决思路,链表作为一种数据结构,在Leetcode系统上作答是不需要自己去定义节点和链表的类,一般是会在注释中给出定义的提示的,我们只需要按照提示去创建节点就好,为了更好地理解这种算法的优势以及劣势,我们该是需要掌握关于链表的增删查改函数怎么写。
1. 单向链表 单向链表就是最简单的一种形态,每个节点属性为自身的值(val)和指向下一节点地址的指针(next),节点通过指针相连成链表
1.1 创建链表容器和节点 链表相当于一个容器,里面装着节点,节点也可以看成一个容器,在单向链表中,节点里面装着val和next
创建节点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Node (): def __init__ (self, val ): self .val = val self .next = None
用类来创建节点,初始化有两个属性,只需要调用这个类就可以形象的创建出节点
创建链表容器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class SingleLinkList (): def __init__ (self ): self ._head = None
初始状态下,链表中只装着空值的_head节点,等待传入上面创建的node节点
1.2 创建链表 第一步:实例化对象创建一个容器
1 link_list = SingleLinkList()
第二步:创建节点,此时只是产生一个节点,并没有加进链表
1 2 3 node1 = Node(100 ) node2 = Node(200 )
第三步:将节点插入链表中,现在第一个结点是node1
将第一个节点node1指向node2
第四步:访问链表节点数据
第一个节点
1 print (link_list._head.val)
第二个节点
1 print (link_list._head.next .val)
1.3 单向链表的操作 这里是直接在链表容器类中添加方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 class SingleLinkList (): def __init__ (self ): self ._head = None def is_empty (self ): return self ._head is None def length (self ): cur = self ._head count = 0 while cur is not None : count += 1 cur = cur.next return count def vals (self ): cur = self ._head while cur is not None : yield cur.val cur = cur.next def add (self,val ): node_add = Node(val) node_add.next = self ._head self ._head = node_add def append (self,val ): node_append = Node(val) if self .is_empty(): self ._head = node_append else : cur = self ._head while cur.next is not None : cur = cur.next cur.next = node_append def insert (self,index,val ): if index <= 0 : self .add(val) elif index > (self .length() - 1 ): self .append(val) else : node = Node(val) cur = self ._head for _ in range (index-1 ): cur = cur.next node.next = cur.next cur.next = node def remove (self,val ): cur = self ._head pre = None while cur is not None : if cur.val == val: if not pre: self ._head = cur.next else : pre.next = cur.next return True else : pre = cur cur = cur.next def find (self,val ): return val in self .val
链表的增删查改只要是应用了指针的思想,这里拿出节点插入指定位置和删除指定位置节点来做简单分析
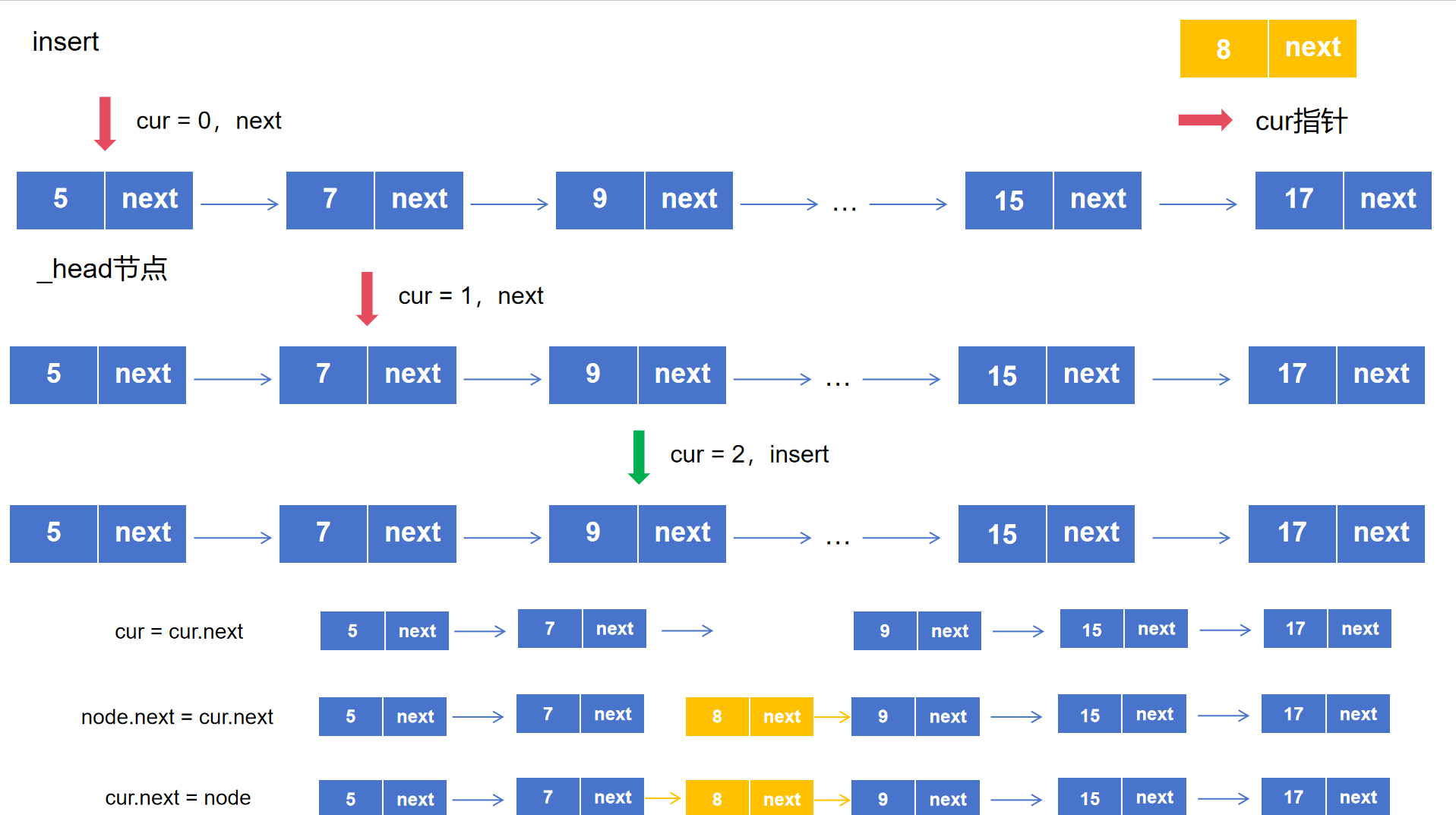
1.3.1 节点插入指定位置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 def insert (self,index,val ): if index <= 0 : self .add(val) elif index > (self .length() - 1 ): self .append(val) else : node = Node(val) cur = self ._head for _ in range (index-1 ): cur = cur.next node.next = cur.next cur.next = node
图解:
为了保证插入前后,链表其他节点值不变,插入过程中首先断开insert处的节点,插入的新节点先链接后方链表,再连接前方链表
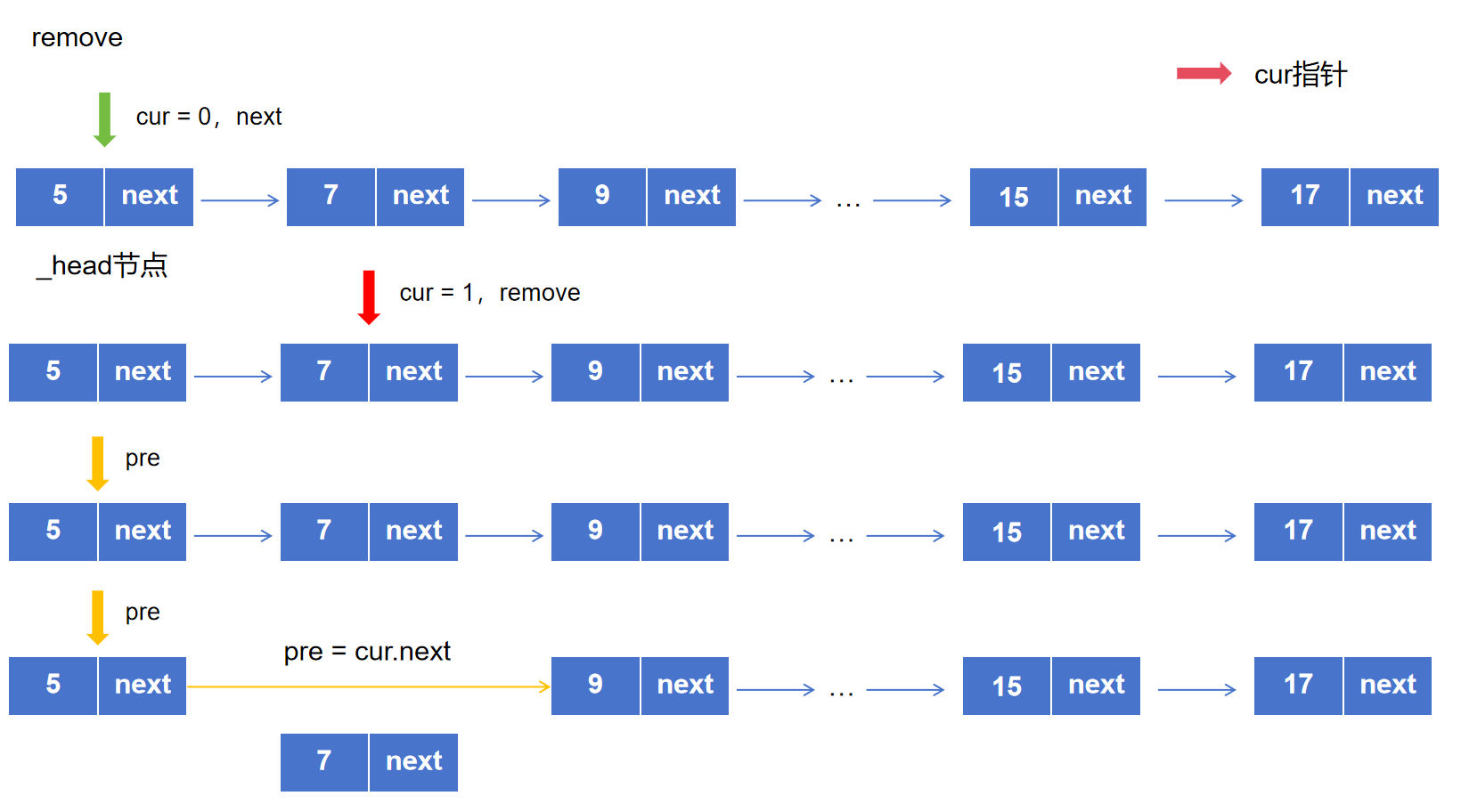
1.3.2 删除指定位置节点1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 def remove (self,val ): cur = self ._head pre = None while cur is not None : if cur.val == val: if not pre: self ._head = cur.next else : pre.next = cur.next return True else : pre = cur cur = cur.next
图解:
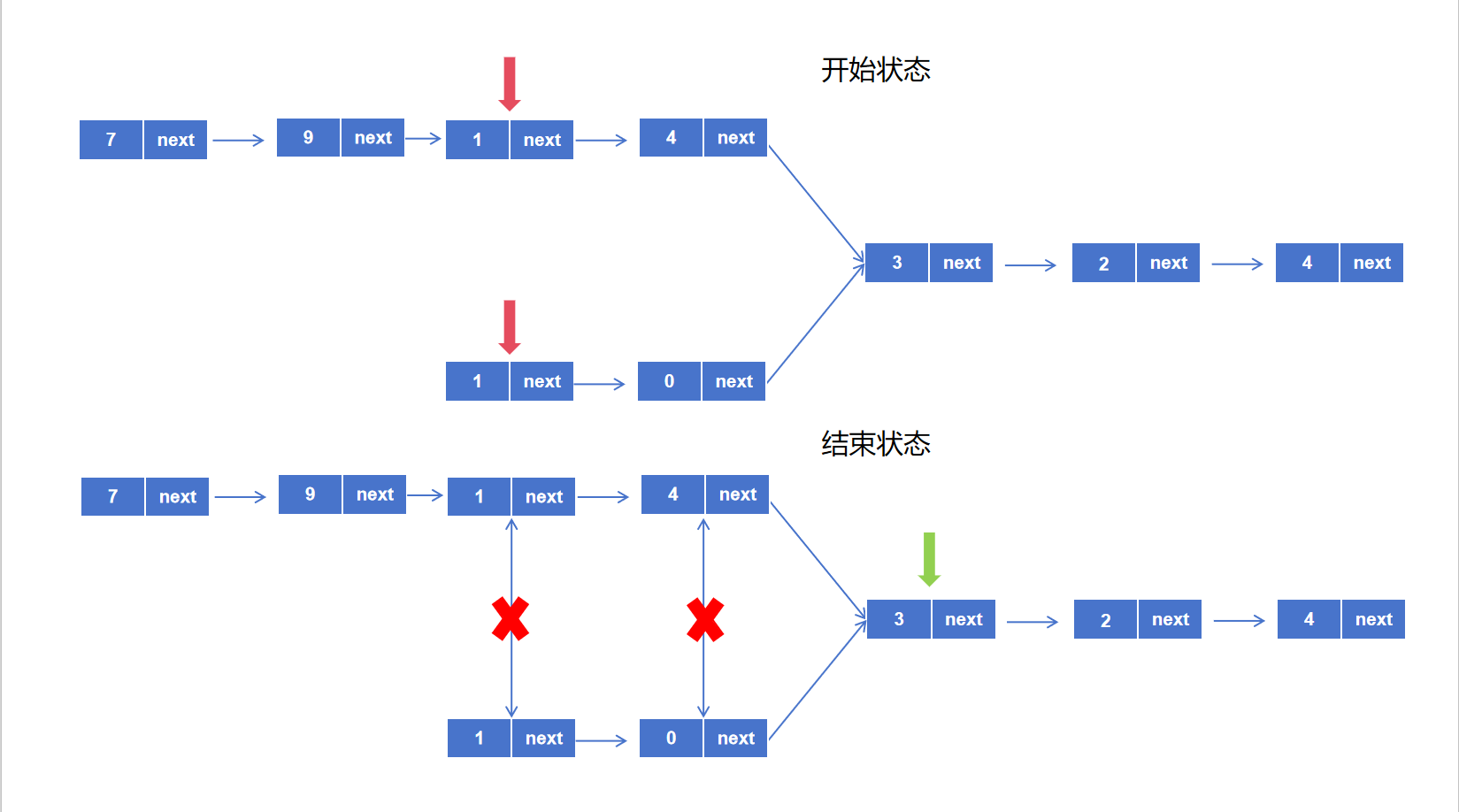
1.4 Leetcode实战 (1)相交链表 Leetcode题号:160
解法一: 思路:这个题求的是相交链表,既相交过后两个链表将合并指向一个值,那么相交后最后到达终点经历的的节点数是一样的,判断相交的条件是两个链表第一个相同地址,根据这两个特点,我们可以设计出一条思路:
先让两条链表的起点在距离相交节点相同数量的节点上,既让长的那条链表先移动一定距离,然后两条链表共同向前移动,等到有节点相等时,即为相交链表。
图解:
但是要注意一个细节,链表节点判定相等的条件是指向同一个地址,而不是同一个值,因此代码中不是比较val
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution (object ): def getIntersectionNode (self, headA, headB ): """ :type headA, headB: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ def length (head ): count = 0 cur = head while cur is not None : count += 1 cur = cur.next return count la = length(headA) lb = length(headB) cur_a, cur_b = headA, headB if lb > la: la, lb = lb, la cur_a, cur_b = cur_b, cur_a gap = la - lb while gap != 0 : cur_a = cur_a.next gap -= 1 while cur_a is not None and cur_b is not None : if cur_a == cur_b: return cur_a cur_a = cur_a.next cur_b = cur_b.next return None
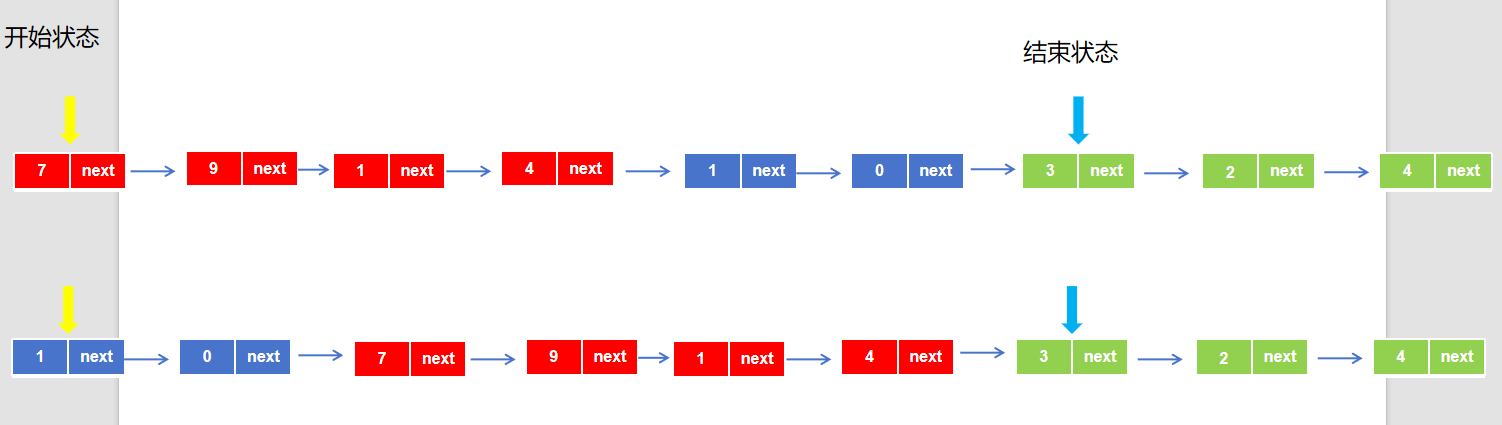
解法二: 图解:
不难看出,解这道题的关键其实就是对齐相交节点 ,那么我们将第一条链表的所有节点遍历完,再去遍历第二条链表的所有节点,与先二后一所遍历的节点的节点数是一样的,但是在第二次遍历到相同节点时是同时的,这就达到了我们对齐链表的目的,上面图解画的不是很准确,但是基本思想是相同的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution (object ): def getIntersectionNode (self, headA, headB ): """ :type headA, headB: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ def length (head ): count = 0 cur = head while cur is not None : count += 1 cur = cur.next return count cur_a = headA cur_b = headB length_tol = length(headA) + length(headB) count = 0 while count < length_tol: if cur_a == cur_b: return cur_a else : count += 1 if cur_a.next is not None : cur_a = cur_a.next else : cur_a = headB if cur_b.next is not None : cur_b = cur_b.next else : cur_b = headA
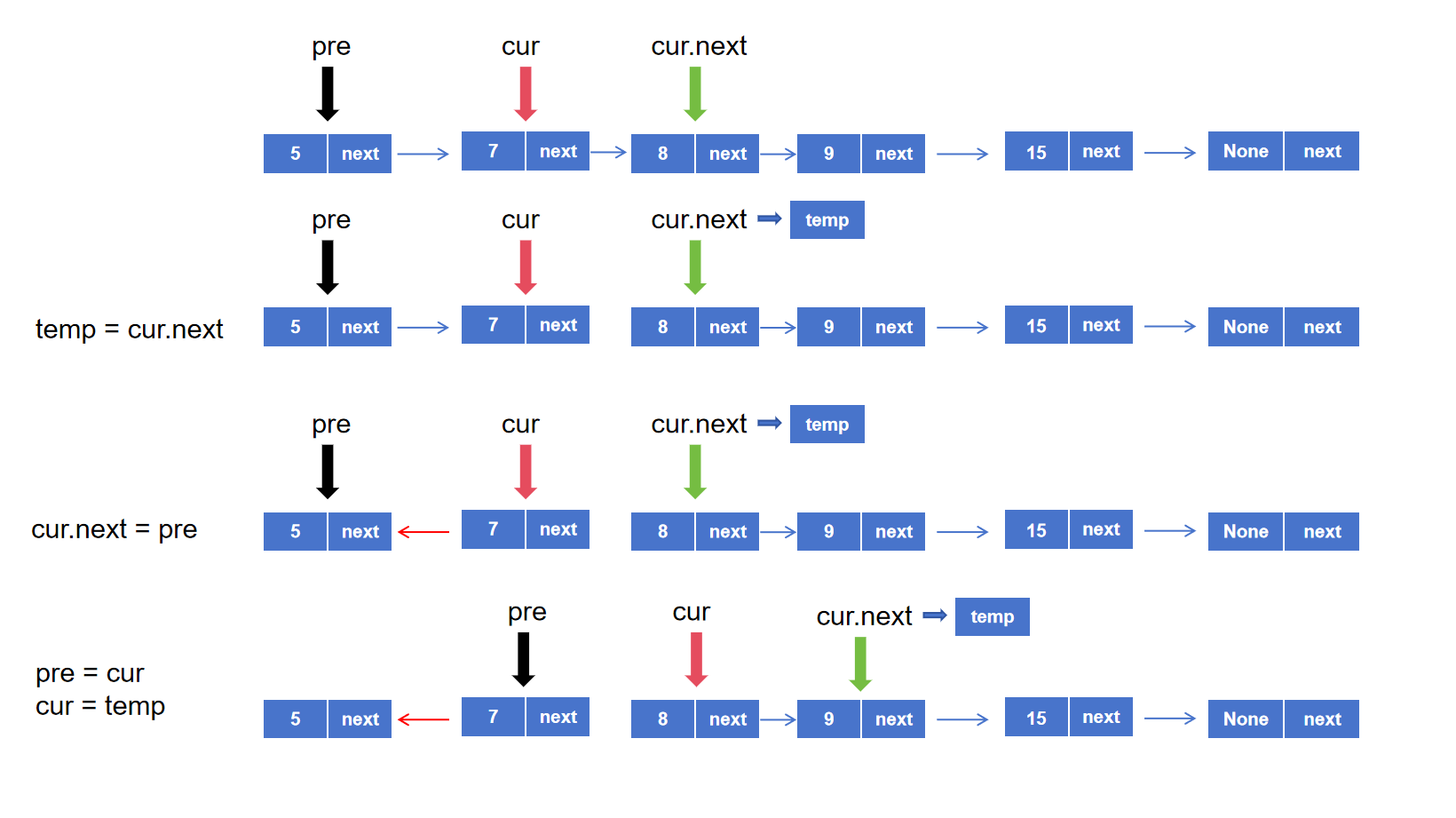
(2)反转链表 Leetcode题号:206
这是一个比较经典的题目,要求将链表反转,既头结点变尾节点,可以抽象的认为反转链表就是反转链表的箭头,这个题主要难点在于理清楚临时变量的作用
图解:
临时变量存储的是cur.next,既cur之后节点的信息,不至于在cur.next = pre的时候丢失 cur.next原本指向的后续节点
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution (object ): def reverseList (self, head ): """ :type head: Optional[ListNode] :rtype: Optional[ListNode] """ pre = None cur = head while cur is not None : temp = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = temp return pre
至于最后为什么返回的是pre,是因为循环停止到最后一个cur节点时,代码仍然执行了pre = cur,cur = temp,也就是指针向后又移了一位,此时cur = None,而pre才是原链表的最后一个节点,既新链表的第一个节点
记录一个题:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 number_to_letter = {chr (96 + i): i for i in range (1 , 27 )} def fn (str1,str2,number_to_letter ): steps = [] length = len (str1) for i in range (len (str2[:length])+1 ): step = 0 str2_ = str2[i:i+length] if length > len (str2_): break print (str1,str2_) for i in range (len (str1)): left = str1[i] right = str2_[i] diff = abs (number_to_letter[left] - number_to_letter[right]) if diff >= 13 : diff = 26 -diff step+=diff steps.append(step) return steps str1 = "ddhnayalcs" str2 = "tffivyioexdqifmeadcz" steps = fn(str1,str2,number_to_letter) min (steps)